Which Mountain is called the roof of the world?
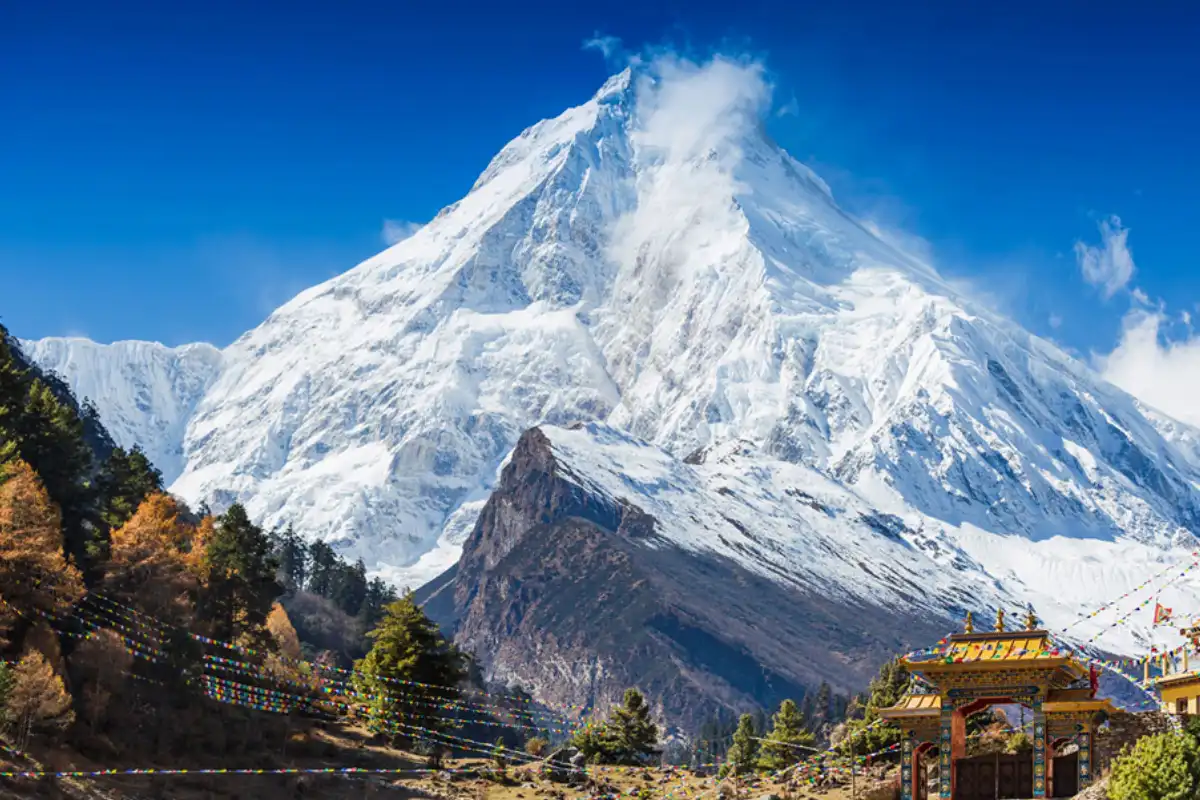

Which Mountain is called the roof of the world?
The Pamir Mountains are famously known as the “Roof of the World”, also called “Bam-i-Duniya” in Persian. They are located in Central Asia, mainly in Tajikistan, and extend into Afghanistan, China, and Kyrgyzstan.
The Pamirs form one of the highest plateaus on Earth and connect several major mountain ranges, including the Himalayas, Karakoram, Hindu Kush, Kunlun, and Tian Shan.
Why Are the Pamir Mountains Called the Roof of the World?
The Pamirs are called the Roof of the World because they sit at the central meeting point of Asia’s highest mountain ranges. The plateau’s average elevation is over 4,000 metres (13,000 feet), with several peaks above 7,000 metres (23,000 feet).
The Persian term “Bam-i-Duniya” literally means “Roof of the World”, reflecting both its high altitude and its position as the geographical heart of Asia. Early explorers, traders, and travellers on the Silk Road used this name to describe the vast highlands where the sky seems closest to the Earth.
Where Are the Pamir Mountains Located?
The Pamirs are mainly in eastern Tajikistan, stretching into Afghanistan, China (Xinjiang), and Kyrgyzstan. The heart of the region is the Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Province of Tajikistan. Key areas include the Wakhan Corridor in Afghanistan and the Murghab Plateau in Tajikistan.
The Pamirs’ location at the crossroads of Central and South Asia makes them a vital link between Asia’s highest mountain systems.
What Is the Highest Peak in the Pamirs?
The highest peak is Ismoil Somoni Peak (formerly Communism Peak) at 7,495 meters (24,590 feet). It is named after Ismoil Somoni, the founder of the first Persian Empire in Central Asia. Other notable peaks include Independence Peak (7,134 meters) and Kaufman Peak (6,723 meters). These towering mountains make the Pamirs one of the most elevated regions on Earth.
Historical Background of the Name “Roof of the World”
The name “Roof of the World” or “Bam-i-Duniya” has been used for centuries by Persian and Central Asian travellers. In the 19th century, Western explorers also adopted the term to describe the Pamir Plateau’s high elevation and remote location. The name reflects both its physical grandeur and its symbolic significance as the highest and most remote part of the continent.
Climate and Geography of the Pamirs
The Pamir Mountains have a harsh alpine climate, with long, cold winters and short, mild summers. Winter temperatures can drop below -40°C, and many valleys are snow-covered year-round. The Pamirs are home to the Fedchenko Glacier, the largest glacier outside the polar regions, stretching over 77 kilometers. The combination of icy peaks, glaciers, and high-altitude deserts makes this one of the most dramatic and challenging environments on Earth.
Interesting Facts About the Pamir Mountains
Bam-i-Duniya – The Persian name highlights the region as one of the highest inhabited areas on Earth.
Meeting Point of Great Ranges – The Pamirs connect five major mountain ranges into one network.
Home to the Fedchenko Glacier – The glacier is over 77 kilometres long, the largest outside the polar regions.
Ancient Trade Route – The Pamirs were a key part of the Silk Road, used for centuries to trade silk, spices, and precious stones.
High-Altitude Living – Villages here are among the highest permanent settlements in the world, with people living above 3,500 metres.
The Pamir Mountains truly live up to their name, the “Roof of the World”, offering breathtaking landscapes, a rich history, and a unique high-altitude lifestyle.
Read More: New WhatsApp Desktop App Now Released in Pakistan
Catch all the Trending News, Breaking News Event and Trending News Updates on GTV News
Join Our Whatsapp Channel GTV Whatsapp Official Channel to get the Daily News Update & Follow us on Google News.